
For example, if you declare a function called 'factorial':
The following characters cannot be used in filenames:
MATLAB SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES IN FOLDER WINDOWS
MATLAB for Windows retains the file naming constraints set by DOS.You can name files whatever you want (usually simpler is better though), with a few exceptions: m file, you can use file -> open, or typeįile Naming Constraints To get the name of this and all other environment variables, type "who". mat file is stored with the same name as the variable originally had when it was saved. The file must be in a recognized directory (usually your current directory, but at least one for which the path has been set). mat file (within a function, for example) is to type: m file click "open", whereas to import data from a data file select "import data." and follow the wizard's instructions.Īn alternative way to load a saved. Likewise, there are many ways to load files into the workspace. The files are saved in your current directory, as seen on the top of the window. diary - saves all the text input in the command window to a text file.hgsave - saves figures to files, *.fig by default.save - saves data to files, *.mat by default.There are many ways to save to files in MATLAB. If you forget to do this and attempt to access a file that is not part of your defined path list, you will get an 'undefined function' error. Then look for and select the folder you want. You could also go to "add folder with subfolders.", if you're adding an entire group, as you would if you were installing a toolbox.

If you still want to call a function but it is not part of the current directory, you must define it using MATLAB's 'set path' utility. The current directory is also the directory in which MATLAB will first look for a data file. Therefore if you have multiple folders and each of them has an M-file of the same name, there will not be a discrepancy if you set the current directory beforehand. The current directory is the directory MATLAB will look in first for a function you try to call. After you start MATLAB, change the current directory by either using the toolbar at the left-hand side of the screen, or entering the path in the bar at the top. By default, unless you edit the MATLAB shortcut, the current directory will be. It is necessary to declare a current directory before saving a file, loading a file, or running an M-file. 1 The Current Directory and Defined Path.Matlab operates on text files very effectively and efficiently. We can read the text file data in various ways as per our needs and as per application need. But by using Matlab we can easily import and export the data from the text file to Matlab or Matlab to a text file. To deal with text files in Matlab is a little difficult. This example shows that we can perform operations on existing data and we can read the same. To read the file we use dlm read function. Data is written in the text file ‘file4’. In this example, input data is declared by using another one variable, which is ‘data’ (data=).
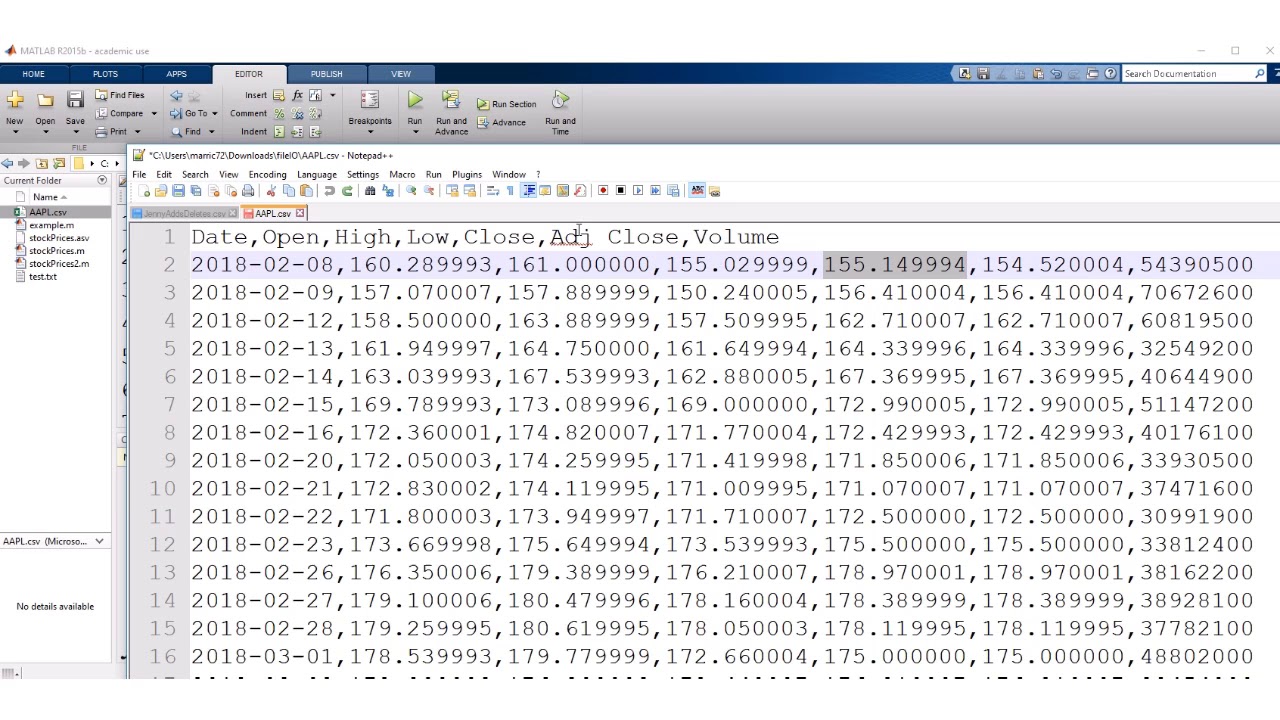
In this example input data is declared by using another two variables, which is ‘data’ (data1= and data2 = Data is written in text file ‘file2’ and read the same.ĭata1 = ĭlmwrite ( ' file3.txt ', ) In this example input data is declared by using another variable, which is ‘ data ’ (data = ). Here we are using a simple method to create the file and then we use dlmread command to read text file1.ĭlmwrite ( ' file1.txt ', ) So it will create one text file in the current directory. In this example, the text file is ‘ file1.txt ’ and data added to the file is. Given below are the examples of dlmread in Matlab: Example #1 Declare variable to read file (optional).Create a text file by using ‘dlmwrite’ syntax ( dlmwrite (filename, ).We can also modify the existing text file by applying some operations on data. These files can be written by passing parameter lists, direct data. There are various ways to write and read text files. To read any text file in Matlab first we need to create that file with some data into it. Hadoop, Data Science, Statistics & othersĭlmread (filename, ) How does dlmread work in Matlab?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
